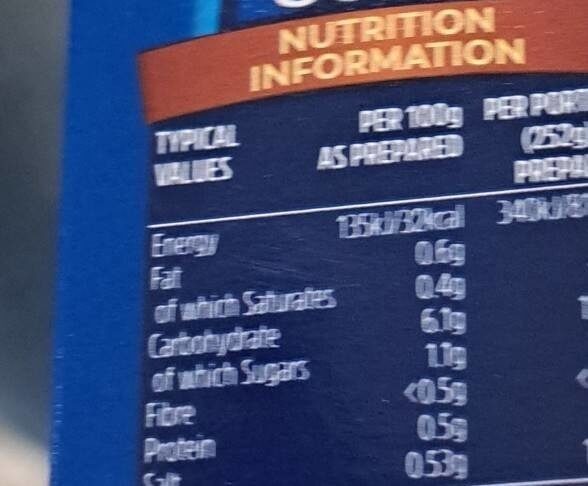
Beef and Tomato soup - Batchelors
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barcode: 5000354402722 (EAN / EAN-13)
Brands: Batchelors
Countries where sold: United Kingdom
Matching with your preferences
Environment
Packaging
Transportation
Threatened species
Report a problem
Data sources
Product added on by inf
Last edit of product page on by segundo.
Product page also edited by kiliweb, vaporous, yuka.sY2b0xO6T85zoF3NwEKvllRCSvTsox70HiHko3WmzefVNJf5evJRz9KqM6s.
If the data is incomplete or incorrect, you can complete or correct it by editing this page.