Help us make food transparency the norm!
As a non-profit organization, we depend on your donations to continue informing consumers around the world about what they eat.
The food revolution starts with you!
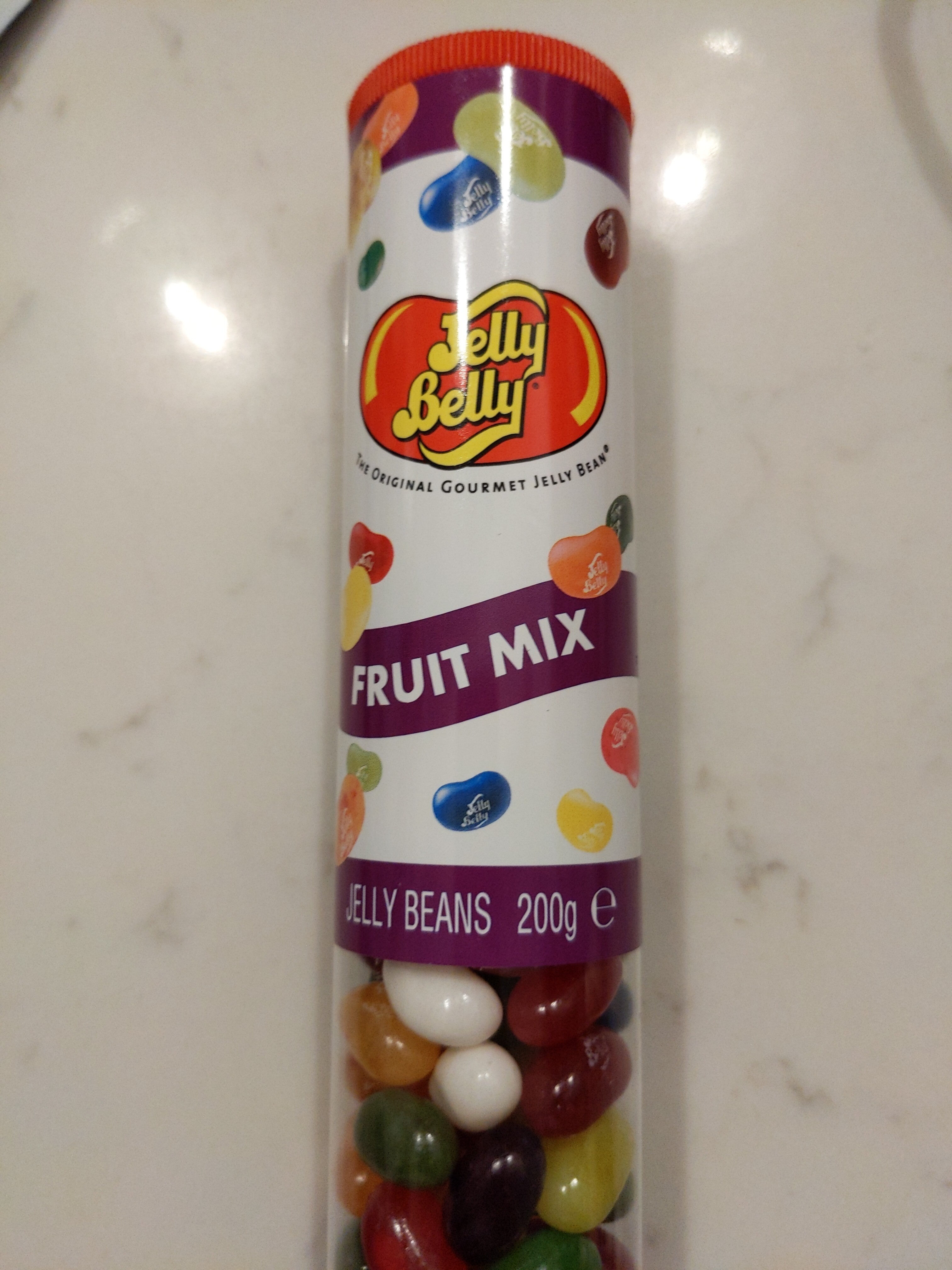
Fruit Mix Jelly Beans - Jelly Belly - 200g
Fruit Mix Jelly Beans - Jelly Belly - 200g
This product page is not complete. You can help to complete it by editing it and adding more data from the photos we have, or by taking more photos using the app for Android or iPhone/iPad. Thank you!
×
Barcode: 5036642077808 (EAN / EAN-13)
Quantity: 200g
Brands: Jelly Belly
Categories: Snacks, Sweet snacks, Confectioneries, Candies, Gummi candies
Countries where sold: United Kingdom
Matching with your preferences
Health
Ingredients
-
44 ingredients
Sugar, glucose syrup, modified cornstarch, acidity regulators (E270, E296, E325, E330, E331), raspberry puree, flavourings, peach puree concentrate, blueberry puree, fruit and vegetable concentrates (spirulina, carrot, black currant, apple, pumpkin, hibiscus, grape), banana puree, lemon puree, grape juice concentrate, apple juice concentrate, glazing agents (E901, E903, E904), pear juice concentrate, watermelon juice concentrate, tangerine juice concentrate, pomegranate juice concentrate, colours (E100, E150a, E160a, E162, E171), grapefruit juice concentrate, cherry juice concentrate, dried coconut powder, lime juice concentrate, tapioca dextrin.Allergens: Apple
Food processing
-
Ultra processed foods
Elements that indicate the product is in the 4 - Ultra processed food and drink products group:
- Additive: E100 - Curcumin
- Additive: E1400 - Dextrin
- Additive: E150a - Plain caramel
- Additive: E160a - Carotene
- Additive: E162 - Beetroot red
- Additive: E171 - Titanium dioxide
- Additive: E325 - Sodium lactate
- Additive: E901 - White and yellow beeswax
- Additive: E903 - Carnauba wax
- Additive: E904 - Shellac
- Ingredient: Colour
- Ingredient: Flavouring
- Ingredient: Glazing agent
- Ingredient: Glucose
- Ingredient: Glucose syrup
Food products are classified into 4 groups according to their degree of processing:
- Unprocessed or minimally processed foods
- Processed culinary ingredients
- Processed foods
- Ultra processed foods
The determination of the group is based on the category of the product and on the ingredients it contains.
Additives
-
E1400 - Dextrin
Dextrin: Dextrins are a group of low-molecular-weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch or glycogen. Dextrins are mixtures of polymers of D-glucose units linked by α--1→4- or α--1→6- glycosidic bonds. Dextrins can be produced from starch using enzymes like amylases, as during digestion in the human body and during malting and mashing, or by applying dry heat under acidic conditions -pyrolysis or roasting-. The latter process is used industrially, and also occurs on the surface of bread during the baking process, contributing to flavor, color and crispness. Dextrins produced by heat are also known as pyrodextrins. The starch hydrolyses during roasting under acidic conditions, and short-chained starch parts partially rebranch with α--1‚6- bonds to the degraded starch molecule. See also Maillard Reaction. Dextrins are white, yellow, or brown powders that are partially or fully water-soluble, yielding optically active solutions of low viscosity. Most of them can be detected with iodine solution, giving a red coloration; one distinguishes erythrodextrin -dextrin that colours red- and achrodextrin -giving no colour-. White and yellow dextrins from starch roasted with little or no acid are called British gum.Source: Wikipedia
-
E160a - Carotene
Carotene: The term carotene -also carotin, from the Latin carota, "carrot"- is used for many related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but in general cannot be made by animals -with the exception of some aphids and spider mites which acquired the synthesizing genes from fungi-. Carotenes are photosynthetic pigments important for photosynthesis. Carotenes contain no oxygen atoms. They absorb ultraviolet, violet, and blue light and scatter orange or red light, and -in low concentrations- yellow light. Carotenes are responsible for the orange colour of the carrot, for which this class of chemicals is named, and for the colours of many other fruits, vegetables and fungi -for example, sweet potatoes, chanterelle and orange cantaloupe melon-. Carotenes are also responsible for the orange -but not all of the yellow- colours in dry foliage. They also -in lower concentrations- impart the yellow coloration to milk-fat and butter. Omnivorous animal species which are relatively poor converters of coloured dietary carotenoids to colourless retinoids have yellowed-coloured body fat, as a result of the carotenoid retention from the vegetable portion of their diet. The typical yellow-coloured fat of humans and chickens is a result of fat storage of carotenes from their diets. Carotenes contribute to photosynthesis by transmitting the light energy they absorb to chlorophyll. They also protect plant tissues by helping to absorb the energy from singlet oxygen, an excited form of the oxygen molecule O2 which is formed during photosynthesis. β-Carotene is composed of two retinyl groups, and is broken down in the mucosa of the human small intestine by β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase to retinal, a form of vitamin A. β-Carotene can be stored in the liver and body fat and converted to retinal as needed, thus making it a form of vitamin A for humans and some other mammals. The carotenes α-carotene and γ-carotene, due to their single retinyl group -β-ionone ring-, also have some vitamin A activity -though less than β-carotene-, as does the xanthophyll carotenoid β-cryptoxanthin. All other carotenoids, including lycopene, have no beta-ring and thus no vitamin A activity -although they may have antioxidant activity and thus biological activity in other ways-. Animal species differ greatly in their ability to convert retinyl -beta-ionone- containing carotenoids to retinals. Carnivores in general are poor converters of dietary ionone-containing carotenoids. Pure carnivores such as ferrets lack β-carotene 15‚15'-monooxygenase and cannot convert any carotenoids to retinals at all -resulting in carotenes not being a form of vitamin A for this species-; while cats can convert a trace of β-carotene to retinol, although the amount is totally insufficient for meeting their daily retinol needs.Source: Wikipedia
-
E162 - Beetroot red
Betanin: Betanin, or Beetroot Red, is a red glycosidic food dye obtained from beets; its aglycone, obtained by hydrolyzing away the glucose molecule, is betanidin. As a food additive, its E number is E162. The color of betanin depends on pH; between four and five it is bright bluish-red, becoming blue-violet as the pH increases. Once the pH reaches alkaline levels betanin degrades by hydrolysis, resulting in a yellow-brown color. Betanin is a betalain pigment, together with isobetanin, probetanin, and neobetanin. Other pigments contained in beet are indicaxanthin and vulgaxanthins.Source: Wikipedia
-
E171 - Titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide: Titanium dioxide, also known as titaniumIV oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO2. When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 -PW6-, or CI 77891. Generally, it is sourced from ilmenite, rutile and anatase. It has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million metric tons. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and the oxide has been valued at $13.2 billion.Source: Wikipedia
-
E270 - Lactic acid
Lactic acid: Lactic acid is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH-OH-COOH. In its solid state, it is white and water-soluble. In its liquid state, it is colorless. It is produced both naturally and synthetically. With a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group, lactic acid is classified as an alpha-hydroxy acid -AHA-. In the form of its conjugate base called lactate, it plays a role in several biochemical processes. In solution, it can ionize a proton from the carboxyl group, producing the lactate ion CH3CH-OH-CO−2. Compared to acetic acid, its pKa is 1 unit less, meaning lactic acid deprotonates ten times more easily than acetic acid does. This higher acidity is the consequence of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the α-hydroxyl and the carboxylate group. Lactic acid is chiral, consisting of two optical isomers. One is known as L--+--lactic acid or -S--lactic acid and the other, its mirror image, is D--−--lactic acid or -R--lactic acid. A mixture of the two in equal amounts is called DL-lactic acid, or racemic lactic acid. Lactic acid is hygroscopic. DL-lactic acid is miscible with water and with ethanol above its melting point which is around 17 or 18 °C. D-lactic acid and L-lactic acid have a higher melting point. In animals, L-lactate is constantly produced from pyruvate via the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase -LDH- in a process of fermentation during normal metabolism and exercise. It does not increase in concentration until the rate of lactate production exceeds the rate of lactate removal, which is governed by a number of factors, including monocarboxylate transporters, concentration and isoform of LDH, and oxidative capacity of tissues. The concentration of blood lactate is usually 1–2 mM at rest, but can rise to over 20 mM during intense exertion and as high as 25 mM afterward. In addition to other biological roles, L-lactic acid is the primary endogenous agonist of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 1 -HCA1-, which is a Gi/o-coupled G protein-coupled receptor -GPCR-.In industry, lactic acid fermentation is performed by lactic acid bacteria, which convert simple carbohydrates such as glucose, sucrose, or galactose to lactic acid. These bacteria can also grow in the mouth; the acid they produce is responsible for the tooth decay known as caries. In medicine, lactate is one of the main components of lactated Ringer's solution and Hartmann's solution. These intravenous fluids consist of sodium and potassium cations along with lactate and chloride anions in solution with distilled water, generally in concentrations isotonic with human blood. It is most commonly used for fluid resuscitation after blood loss due to trauma, surgery, or burns.Source: Wikipedia
-
E296 - Malic acid
Malic acid: Malic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H6O5. It is a dicarboxylic acid that is made by all living organisms, contributes to the pleasantly sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms -L- and D-enantiomers-, though only the L-isomer exists naturally. The salts and esters of malic acid are known as malates. The malate anion is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle.Source: Wikipedia
-
E325 - Sodium lactate
Sodium lactate: Sodium lactate is the sodium salt of lactic acid, and has a mild saline taste. It is produced by fermentation of a sugar source, such as corn or beets, and then, by neutralizing the resulting lactic acid to create a compound having the formula NaC3H5O3.Source: Wikipedia
-
E330 - Citric acid
Citric acid is a natural organic acid found in citrus fruits such as lemons, oranges, and limes.
It is widely used in the food industry as a flavor enhancer, acidulant, and preservative due to its tart and refreshing taste.
Citric acid is safe for consumption when used in moderation and is considered a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) food additive by regulatory agencies worldwide.
-
E331 - Sodium citrates
Sodium citrate: Sodium citrate may refer to any of the sodium salts of citrate -though most commonly the third-: Monosodium citrate Disodium citrate Trisodium citrateThe three forms of the salt are collectively known by the E number E331. Sodium citrates are used as acidity regulators in food and drinks, and also as emulsifiers for oils. They enable cheeses to melt without becoming greasy.Source: Wikipedia
-
E901 - White and yellow beeswax
Beeswax: Beeswax -cera alba- is a natural wax produced by honey bees of the genus Apis. The wax is formed into "scales" by eight wax-producing glands in the abdominal segments of worker bees, which discard it in or at the hive. The hive workers collect and use it to form cells for honey storage and larval and pupal protection within the beehive. Chemically, beeswax consists mainly of esters of fatty acids and various long-chain alcohols. Beeswax has long-standing applications in human food and flavoring. For example, it is used as a glazing agent or as a light/heat source. It is edible, in the sense of having similar negligible toxicity to plant waxes, and is approved for food use in most countries and the European Union under the E number E901. However, the wax monoesters in beeswax are poorly hydrolysed in the guts of humans and other mammals, so they have insignificant nutritional value. Some birds, such as honeyguides, can digest beeswax. Beeswax is the main diet of wax moth larvae.Source: Wikipedia
-
E903 - Carnauba wax
Carnauba wax: Carnauba -; Portuguese: carnaúba [kaʁnɐˈubɐ]-, also called Brazil wax and palm wax, is a wax of the leaves of the palm Copernicia prunifera -Synonym: Copernicia cerifera-, a plant native to and grown only in the northeastern Brazilian states of Piauí, Ceará, Maranhão, Bahia, and Rio Grande do Norte. It is known as "queen of waxes" and in its pure state, usually comes in the form of hard yellow-brown flakes. It is obtained from the leaves of the carnauba palm by collecting and drying them, beating them to loosen the wax, then refining and bleaching the wax.Source: Wikipedia
-
E904 - Shellac
Shellac: Shellac is a resin secreted by the female lac bug, on trees in the forests of India and Thailand. It is processed and sold as dry flakes -pictured- and dissolved in alcohol to make liquid shellac, which is used as a brush-on colorant, food glaze and wood finish. Shellac functions as a tough natural primer, sanding sealant, tannin-blocker, odour-blocker, stain, and high-gloss varnish. Shellac was once used in electrical applications as it possesses good insulation qualities and it seals out moisture. Phonograph and 78 rpm gramophone records were made of it until they were replaced by vinyl long-playing records from the 1950s onwards. From the time it replaced oil and wax finishes in the 19th century, shellac was one of the dominant wood finishes in the western world until it was largely replaced by nitrocellulose lacquer in the 1920s and 1930s.Source: Wikipedia
Ingredients analysis
-
May contain palm oil
Ingredients that may contain palm oil: E160a
-
Non-vegan
Non-vegan ingredients: E901, E904
-
Non-vegetarian
Non-vegetarian ingredients: E904
-
Details of the analysis of the ingredients
: Sugar, glucose syrup, modified cornstarch, acidity regulators (e270, e296, e325, e330, e331), raspberry puree, flavourings, peach puree, blueberry, fruit and vegetable concentrates (spirulina, carrot, black currant, apple, pumpkin, hibiscus, grape), banana, lemon puree, grape juice concentrate, apple juice, glazing agents (e901, e903, e904), pear juice concentrate, watermelon, tangerine juice, pomegranate juice, colours (e100, e150a, e160a, e162, e171), grapefruit juice, cherry juice, coconut, lime juice concentrate, tapioca dextrin- Sugar -> en:sugar - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 31016 - percent_min: 4.16666666666667 - percent_max: 100
- glucose syrup -> en:glucose-syrup - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 31016 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 50
- modified cornstarch -> en:modified-corn-starch - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 9510 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 33.3333333333333
- acidity regulators -> en:acidity-regulator - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 25
- e270 -> en:e270 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 25
- e296 -> en:e296 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 12.5
- e325 -> en:e325 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 8.33333333333333
- e330 -> en:e330 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 6.25
- e331 -> en:e331 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- raspberry puree -> en:raspberry-puree - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - ciqual_food_code: 13015 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 20
- flavourings -> en:flavouring - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- peach puree -> en:peach-puree - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13043 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- blueberry -> en:blueberry - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13028 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- fruit and vegetable concentrates -> en:fruit-and-vegetable-concentrates - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- spirulina -> en:spirulina - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 20984 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- carrot -> en:carrot - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 20009 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 2.5
- black currant -> en:blackcurrant - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13007 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.66666666666667
- apple -> en:apple - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13050 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.25
- pumpkin -> en:pumpkin - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 20139 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1
- hibiscus -> en:roselle-flower - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.833333333333333
- grape -> en:grape - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13112 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 0.714285714285714
- banana -> en:banana - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13005 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- lemon puree -> en:lemon-puree - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 13009 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- grape juice concentrate -> en:concentrated-grape-juice - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13112 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- apple juice -> en:apple-juice - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 2074 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- glazing agents -> en:glazing-agent - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- e901 -> en:e901 - vegan: no - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- e903 -> en:e903 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 2.5
- e904 -> en:e904 - vegan: no - vegetarian: no - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.66666666666667
- pear juice concentrate -> en:pear-juice-concentrate - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- watermelon -> en:watermelon - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13036 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- tangerine juice -> en:tangerine-juice - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- pomegranate juice -> en:pomegranate-juice - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- colours -> en:colour - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- e100 -> en:e100 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- e150a -> en:e150a - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 2.5
- e160a -> en:e160a - vegan: maybe - vegetarian: maybe - from_palm_oil: maybe - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.66666666666667
- e162 -> en:e162 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1.25
- e171 -> en:e171 - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 1
- grapefruit juice -> en:grapefruit-juice - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 5
- cherry juice -> en:cherry-juice - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13008 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 4.76190476190476
- coconut -> en:coconut - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_proxy_food_code: 15006 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 4.54545454545455
- lime juice concentrate -> en:lime-juice-concentrate - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - ciqual_food_code: 13067 - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 4.34782608695652
- tapioca dextrin -> en:tapioca-dextrin - vegan: yes - vegetarian: yes - percent_min: 0 - percent_max: 4.16666666666667
Nutrition
-
Poor nutritional quality
⚠ ️Warning: the amount of fiber is not specified, their possible positive contribution to the grade could not be taken into account.⚠ ️Warning: the amount of fruits, vegetables and nuts is not specified on the label, it was estimated from the list of ingredients: 4This product is not considered a beverage for the calculation of the Nutri-Score.
Positive points: 0
- Proteins: 0 / 5 (value: 0, rounded value: 0)
- Fiber: 0 / 5 (value: 0, rounded value: 0)
- Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and colza/walnut/olive oils: 0 / 5 (value: 4.48612123727793, rounded value: 4.5)
Negative points: 14
- Energy: 4 / 10 (value: 1530, rounded value: 1530)
- Sugars: 10 / 10 (value: 61, rounded value: 61)
- Saturated fat: 0 / 10 (value: 0, rounded value: 0)
- Sodium: 0 / 10 (value: 28, rounded value: 28)
The points for proteins are not counted because the negative points are greater or equal to 11.
Nutritional score: (14 - 0)
Nutri-Score:
-
Nutrient levels
-
Fat in low quantity (0%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Saturated fat in low quantity (0%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of fat, especially saturated fats, can raise cholesterol, which increases the risk of heart diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of fat and saturated fat- Choose products with lower fat and saturated fat content.
-
Sugars in high quantity (61%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of sugar can cause weight gain and tooth decay. It also augments the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardio-vascular diseases.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of sugar and sugary drinks- Sugary drinks (such as sodas, fruit beverages, and fruit juices and nectars) should be limited as much as possible (no more than 1 glass a day).
- Choose products with lower sugar content and reduce the consumption of products with added sugars.
-
Salt in low quantity (0.07%)
What you need to know- A high consumption of salt (or sodium) can cause raised blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Many people who have high blood pressure do not know it, as there are often no symptoms.
- Most people consume too much salt (on average 9 to 12 grams per day), around twice the recommended maximum level of intake.
Recommendation: Limit the consumption of salt and salted food- Reduce the quantity of salt used when cooking, and don't salt again at the table.
- Limit the consumption of salty snacks and choose products with lower salt content.
-
-
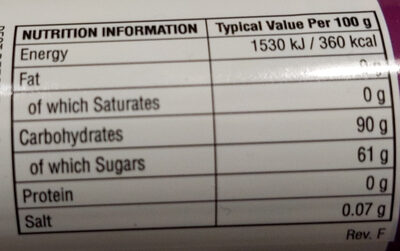
Nutrition facts
Nutrition facts As sold
for 100 g / 100 mlAs sold
per serving (100g)Compared to: Gummi candies Energy 1,530 kj
(360 kcal)1,530 kj
(360 kcal)+7% Fat 0 g 0 g -100% Saturated fat 0 g 0 g -100% Carbohydrates 90 g 90 g +10% Sugars 61 g 61 g +14% Fiber ? ? Proteins 0 g 0 g -100% Salt 0.07 g 0.07 g -30% Fruits‚ vegetables‚ nuts and rapeseed‚ walnut and olive oils (estimate from ingredients list analysis) 4.486 % 4.486 %
Environment
-
Eco-Score B - Low environmental impact
The Eco-Score is an experimental score that summarizes the environmental impacts of food products.→ The Eco-Score was initially developped for France and it is being extended to other European countries. The Eco-Score formula is subject to change as it is regularly improved to make it more precise and better suited to each country.Life cycle analysis
-
Average impact of products of the same category: A (Score: 89/100)
Category: Jelly candy
Category: Jelly candy
- PEF environmental score: 0.21 (the lower the score, the lower the impact)
- including impact on climate change: 1.57 kg CO2 eq/kg of product
Stage Impact Agriculture
51.7 %Processing
31.1 %Packaging
7.6 %Transportation
7.3 %Distribution
2.3 %Consumption
0.0 %
Bonuses and maluses
-
Missing origins of ingredients information
Malus: -5
⚠ ️ The origins of the ingredients of this product are not indicated.
If they are indicated on the packaging, you can modify the product sheet and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.
-
Missing packaging information for this product
Malus: -15
⚠ ️ The information about the packaging of this product is not filled in.⚠ ️ For a more precise calculation of the Eco-Score, you can modify the product page and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.
Eco-Score for this product
-
Impact for this product: B (Score: 69/100)
Product: Fruit Mix Jelly Beans - Jelly Belly - 200g
Life cycle analysis score: 89
Sum of bonuses and maluses: -20
Final score: 69/100
-
Carbon footprint
-
Equal to driving 0.8 km in a petrol car
157 g CO² per 100g of product
The carbon emission figure comes from ADEME's Agribalyse database, for the category: Jelly candy (Source: ADEME Agribalyse Database)
Stage Impact Agriculture
36.9 %Processing
38.1 %Packaging
11.9 %Transportation
12.0 %Distribution
1.1 %Consumption
0.0 %
Packaging
-
Missing packaging information for this product
⚠ ️ The information about the packaging of this product is not filled in.Take a photo of the recycling information Take a photo of the recycling information
Transportation
-
Origins of ingredients
Missing origins of ingredients information
⚠ ️ The origins of the ingredients of this product are not indicated.
If they are indicated on the packaging, you can modify the product sheet and add them.
If you are the manufacturer of this product, you can send us the information with our free platform for producers.Add the origins of ingredients for this product Add the origins of ingredients for this product
Report a problem
-
Incomplete or incorrect information?
Category, labels, ingredients, allergens, nutritional information, photos etc.
If the information does not match the information on the packaging, please complete or correct it. Open Food Facts is a collaborative database, and every contribution is useful for all.
Data sources
Product added on by alexander-sparasci
Last edit of product page on by ecoscore-impact-estimator.
Product page also edited by openfoodfacts-contributors.